|
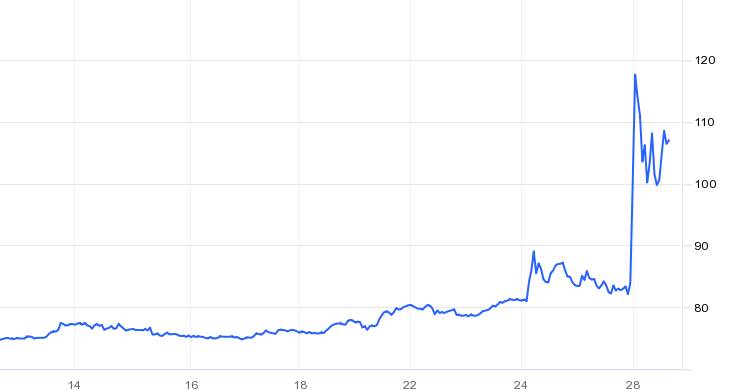
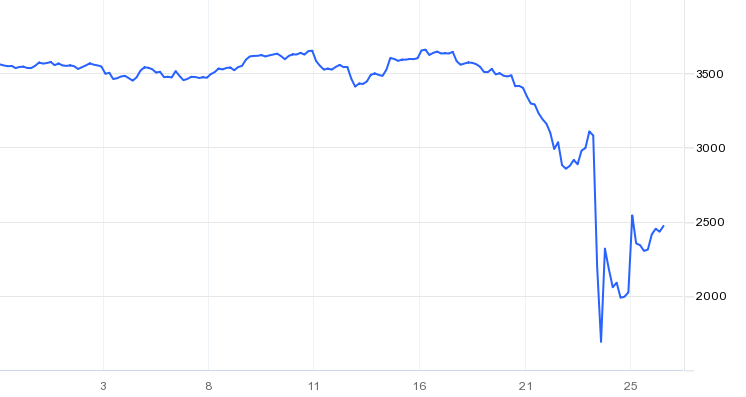
The war in the Ukraine caused by the Russian invasion is the dominant topic around the world. In particular Western states widely underestimated Putin and the likelihood of the Russian invasion. Initial rumours anticipated an invasion from Russia on Monday, 14th February 2022, as Russian troops supposedly retreated. After the invasion did not take place then, there were some signs of relief, which were short-lived. Fears started to grow when Putin acknowledged the separatists in the Eastern Ukraine, more specifically, Donetsk and Luhansk. There were crucial similarities compared to the annexation of the Crimea peninsula in 2014. While this was going on, Western countries threatened Russia with sanctions. Those did not achieve a meaningful impact, as on Thursday morning, the worst case in that situation occurred. Russia invaded the Ukraine from all angles and managed to shutdown their missile defences almost immediately. Russia conquered several parts of the Ukraine extremely quickly and found itself soon on the doors of the capitol, Kyiv. Later that day, sanctions on Russia were imposed by the US, the UK, the G7 states and most other European countries. These included freezing the assets of some of Russian elites, some banks and businesses in the respective countries. This sanctions prohibit being involved in any kind of business with those individuals, banks or businesses. The US also banned individuals from trading Russian sovereign debt. Those sanctions had little impact on the invasion of Russia. Most people hoped the sanctions would be harsher, but at that point Europe was reluctant on banning Russia from SWIFT due to their reliance on Russia’s oil and gas. The invasion truly changed into a war in the city of Kyiv and over time most countries around the world support the Ukraine with additional weapons and ammunition, while some countries even sent soldiers to help defending the country. On Monday, the SWIFT ban from some Russian banks was announced as well as the extension of listed targets and institutions whose assets are frozen. Initially, Russia’s goal was to de-weaponize the country and to replace Zelensky, the prime minister of the Ukraine, by a more pro-Russian government. Russia employed substantial propaganda and legitimized the invasion by calling the Ukraine being full of Nazis among other things. It now seems very questionable whether replacing the government was the initial target, as it feels much more like a full annexation. This puts in particular the Baltic states into a state of alert, as if Putin’s goal to recreate the former Soviet Union, then they are likely the next target. This also explains the harsh threats from Russia when discussions were held whether Finland should become a NATO state. Further unpleasant developments are that China can be considered neutral towards Russia’s actions, as they first supported the Russian invasion given the reasons from Russia. However, they also followed through on Zelensky’s call to talk to Putin on possibilities to resolve this war. After an initial discussion between the Ukraine and Russia was denied by the Ukraine, it seems to be likely that Putin and Zelensky agreed to a meeting. This comes after Russia’s threat of using nuclear warheads. Unsurprisingly, markets reacted with tremendous volatility over the past two weeks. The sanctions on Russia had a detrimental effect on Russia’s economy. The Russian Rubel collapsed by 30% after Western countries announced the SWIFT ban for some Russian banks, after the Rubel has already lost substantially in value since the start of the invasion, as shown in Figure 1. Russia’s equity market also took a huge hit. On the day of the invasion, the MOEX Russia Index dropped by almost 50% from 3,200 down to 1,700. Despite its recovery, it is questionable how Russian equities will perform in the short-term future, as further sanctions are likely and make doing business outside Russia very difficult.
*|MC_PREVIEW_TEXT|*
Comments are closed.
|
|
|
Stone Mountain Capital LTD is authorised and regulated with FRN: 929802 by the Financial Conduct Authority (‘FCA’) in the United Kingdom. The website content is neither an offer to sell nor a solicitation of an offer to buy an interest in any investment or advisory service by Stone Mountain Capital LTD and should be read with the DISCLAIMER. © 2024 Stone Mountain Capital LTD. All rights reserved. |











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
