|
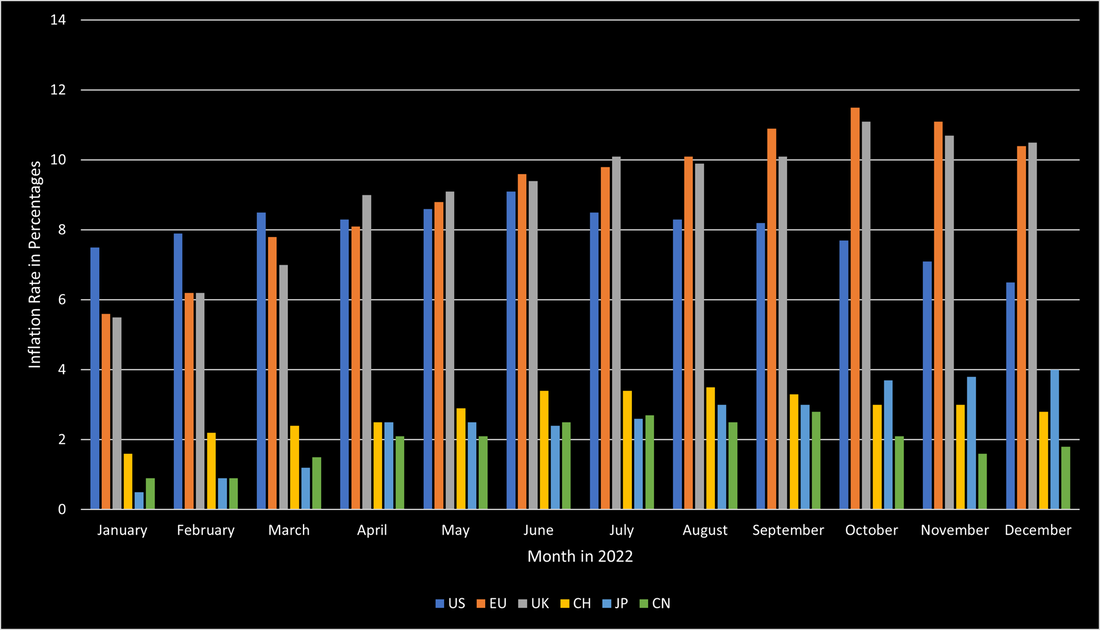
2022 was a year that tested the worldwide economy. The highest inflation in 40 years, unprecedented interest rate hikes, and the invasion of Russia into Ukraine were only some contributors to the hugely difficult year of 2022. In the US, inflation started soaring during 2021 and peaked in the summer of 2022 at 9.1%. Thanks to the central bank’s quick response, inflation has since continuously slowed down and is currently at 6.5%. Europe had significantly more issues handling the inflation crisis. The EU started the year at an inflation rate of slightly above 5.5% and it continued to soar until October 2022 when it reached its peak at 11.5%. The UK was similarly affected, despite the BoE being the fastest-acting central bank to raise interest rates. However, its inflation behaved like the EU’s and soared to its peak at 11.1% in October 2022. Both economies have not been able to reduce inflation below 10% so far. In contrast to the US, European countries were much more affected by the direct impact of the war between Russia and Ukraine. Soaring energy and food prices, for both of which Russia and Ukraine are crucial suppliers, were the main constituents causing the high inflation. Additionally, the ECB did not enjoy as much freedom as the Fed had when raising interest rates. This is in large part due to the high indebtedness of certain European countries that would have gone bankrupt if interest rates would have been raised as much as the US did. Other countries, such as Switzerland, Japan, and China stand out in this discussion, as those countries managed to keep their inflation relatively low. Switzerland managed to avoid such high inflation due to its strong currency, and a limited dependency on fossil fuels. Japan avoided high inflation through the continued quantitative easing by the BoJ. However, in contrast to the other countries, Japan’s inflation is still soaring and poses substantial issues to the country. China avoided high inflation through its rigorous Covid policies and its limited governmental support when Covid emerged. The source of this soaring inflation is a combination of the war but is largely based on unprecedented central bank intervention to save the economy during the early Covid days when large parts of the economy were completely unable to function. Figure 1 shows the inflation levels of the previously mentioned countries during 2022.
ALTERNATIVE MARKETS UPDATE - MID JANUARY 2023 & MACRO AND POLITICAL OUTLOOK 2023 BY MACRO EAGLE11/1/2023
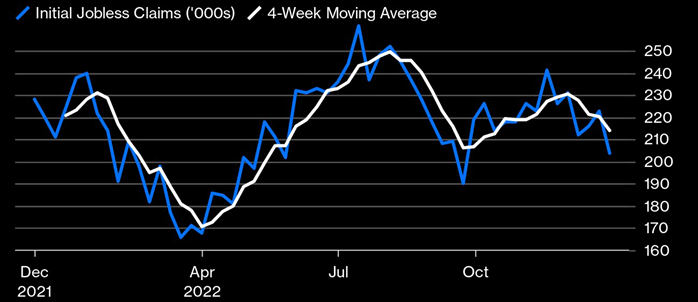
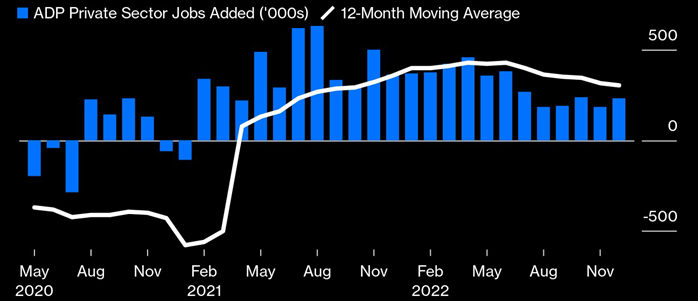
With the currently pessimistic view of 2023, markets are under substantial pressure. Most market participants are expecting a recession in 2023/2024. High inflation, steep interest rate hikes, and historical yield curve inversions are just a few indicators that suggest tough times ahead. However, there are some indicators that provide hope that a larger crisis can be avoided. While inflation is high, it has been steadily decreasing, at least in the US. Rate hikes are also expected to increase only slightly in 2023. Nonetheless, this provides little help in avoiding a recession, as it is still unclear how fast inflation will drop down to the acceptable 2% and below range. Furthermore, interest rates will remain high for 2023 with a low to moderate probability of rate cuts in 2023. These still pressure businesses that are expected to earn less in 2023, as consumers have exhausted most of their resources in dealing with the impact of inflation. The biggest saving grace currently is the labor market, which functions very well. In Western countries, the unemployment rates are close to record lows of the past few decades. In the US and the UK, the unemployment rate is 3.7%. In the EU, the unemployment rate is 6%, while Switzerland sees an unemployment rate of 2.2%. Figure 1 shows the jobless claims in the US in 2022. While there has been some variation during 2022, these were small and at very low levels historically. It is even more promising when addressing the private sector. Since early 2021, the private sector in the US is adding jobs at a constant pace. Figure 2 shows this development.
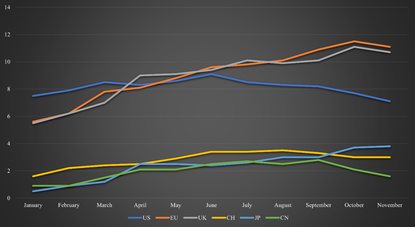
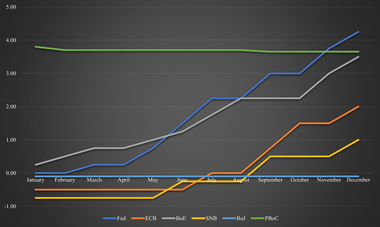
Inflation was a core issue in 2022 and remains to be one in 2023. In the US, inflation started to decline in the summer of 2022 and remains currently at a level of 7.1%. Contrarily, in Europe and the UK, inflation remains a huge issue and has barely declined from its peak in 2022. It remains at 11.1% for the EU and at 10.7% for the UK. The difference between the inflation can largely be attributed to two factors. Firstly, the Fed hikes interest rates more aggressively than its European counterparts. This led to a quicker response to inflation. Secondly, Europe is more directly affected by the war between Russia and Ukraine and is largely dependent on Russian oil and gas, which soared in price following the war. Contrarily to other European countries, Switzerland managed to keep inflation relatively low with a peak in late summer 2022 at 3.5% and 3% currently. Switzerland managed to avoid high inflation due to its strong currency and relatively low demand for fossil fuels, as most of its electricity stems from hydropower and nuclear power. In Asia, both Japan and China also experience limited inflation issues. Japan achieved this through its central bank which continuously intervenes with large-scale monetary easing. Despite the low inflation, Japan is still suffering, as wages remain stagnant unlike in other major economies where it helps offset the higher inflation to some degree. China does not face an inflation problem, due to their different handling of the Covid crisis. Unlike most economies, they did not provide large stimuli to the economy. Additionally, their zero-Covid policy substantially reduced household demands. Figure 1 shows a summary of the inflation rates across the highlighted economies during 2022. Regarding 2023, it is widely expected that inflation, especially in high-inflation countries, will come down. For instance, in the US, it is expected that inflation will be around 4% on average, and close to the 2% Fed target by the end of the year. Inflation forecasts in the EU and the UK are more difficult to estimate, due to their dependency on the war and its outcome. Additionally, unlike in the US, inflation has not really started to decrease. Assuming further strong interventions by the European central banks, it is expected that inflation will drop substantially. The ECB expects the average inflation to be around 5%-6% during 2023 with inflation slightly below 4% by the end of 2023. In the short term, Europe will be under pressure and the measures take time to become effective, as shown in the example of the US. Despite a similar outlook to the US, albeit with a delay of around half a year, it is less promising. One important wildcard is energy prices, which are strongly linked to the war. While the EU managed to get its oil largely from other sources than Russia, it still needs Russia, and gas is not as easily substitutable. With the prospect of Russia’s supply cut and China reopening, prices of energy sources are likely to increase. Depending on the scale, if it occurs, the anticipated target may not be reached and inflation will remain higher than the target. In Switzerland, inflation is expected to remain around the 3% mark for 2023. Given the strong involvement of the BoJ, Japan’s inflation is expected to end the year 2023 below the 2% inflation mark. It is additionally expected that wages will rise for the first time in three decades. Inflation in China is expected to rise to around 2% in 2023. This is a combination of the reopening of the economy and the end of the zero-Covid policy. This will lead to an increase in economic activity and the necessity for further energy. Additionally, the price pressure across will also be felt in China, once demand picks up again. The interest rate hikes by most countries have been another crucial topic during 2022. So far, the hikes have shown limited effectiveness in dealing with soaring inflation. In high-inflation countries, it was effective for the US and had little impact on the European countries. However, this discrepancy is likely due to the steeper hikes in the US and less dependency on the war by the US. The US employed the strongest measures, as it hiked from 0% at the beginning of 2022 to 4.25% at the end of 2022. In contrast, the ECB just started hiking in June 2022 at -0.5%, which increased to 2% by the end of 2022. The BoE employed a mixture of the two. The UK started hiking at the end of 2021 but hiked in smaller steps than the US. Towards the end of 2022, it increased the step size and is currently at 3.5%. Switzerland started hiking earlier than the ECB, despite substantially lower inflation. Switzerland’s prime rate became positive for the first time in years in September 2022. Currently, the prime rate is sitting at 1%. Japan was one of the exceptions, as the BoJ did not hike at all. Its prime rate remains at -0.1%. However, the central bank still strongly intervened in the market as elaborated previously. The People’s Bank of China even lowered its prime lending rate over 2022, albeit to a minimal degree. Currently, the rate is at 3.65%. There is a strong consensus for the year 2023 in the US and Japanese markets. Most market participants expect the Fed to keep raising interest rates to around 5%-5.25%. The Fed is likely to do this in smaller steps than previously. Nonetheless, this level should be reached by the end of Q1 2023. Afterward, a majority of institutions do not expect further hikes or cuts in 2023. The remainder anticipates potential interest rate cuts in Q4 2023. The exact outcome of potentially further hikes or cuts largely depends on the state of the US economy in the latter part of 2023. While the measures seem to be effective and inflation is going down considerably, the risk of a recession is considerable. This largely stems from substantially higher financing costs for businesses, and lower demand from consumers as Covid reserves are exhausted and households feel the pressure from the inflation over the past year. Given that the BoJ has not intervened by raising interest rates, it is not expected that it will in 2023. It is more likely that it will continue its qualitative and quantitative easing philosophy employed so far. In particular, as Japan does not face an imminent inflation problem. With expected wages adjusted, the pressure of inflation should also be eased without a strong necessity to make policy adjustments. For the EU, it is expected that rates will be hiked further to combat the prevalent inflation. Market participants expect interest rates of around 3%, which should be reached during Q2 2023. For the UK, additional hikes of 1% are expected, resulting in interest rates of around 4.5% for 2023. For both economies, no rate cuts are expected in the latter half of 2023. In Switzerland, the SNB is anticipated to hike another 0.5% in 2023 with no rate cuts as well.
|
|
|
Stone Mountain Capital LTD is authorised and regulated with FRN: 929802 by the Financial Conduct Authority (‘FCA’) in the United Kingdom. The website content is neither an offer to sell nor a solicitation of an offer to buy an interest in any investment or advisory service by Stone Mountain Capital LTD and should be read with the DISCLAIMER. © 2024 Stone Mountain Capital LTD. All rights reserved. |



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
