|
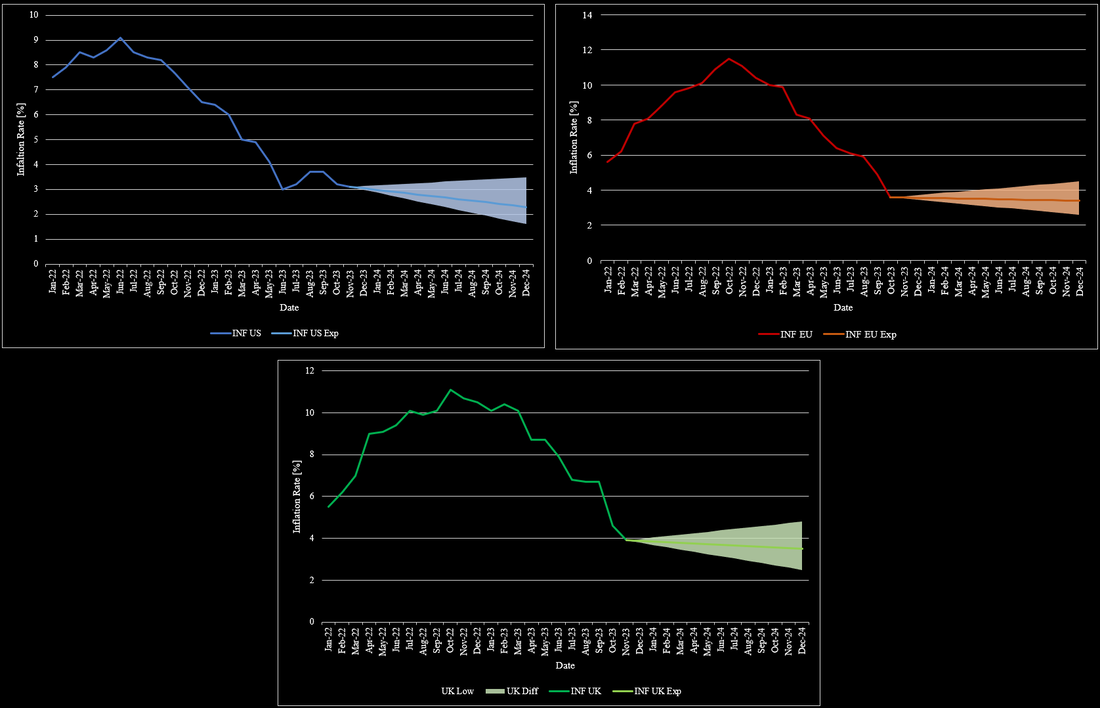
2023 followed the core theme of 2022 with a key focus on inflation and interest rates. At the beginning of 2023, inflation was a huge concern, due to its high level. In the US, inflation was at 6.5% and already declined substantially from its peak in June 2022 at 9.1%. This trend continued in 2023 until it reached its bottom in June 2023 at 3%. Since then, US inflation remained steady between 3% and 4%. The EU and the UK saw a very similar development of inflation throughout 2022. Their respective inflation started at around 5.5% in January 2022 and rose to 10.5% by the end of 2022. As soon as 2023 started, inflation in the EU started to decline and eventually declined to as low as 3.1% in November 2023. Despite this promising development, inflation began to increase again to 3.4% in December 2023. While the UK’s inflation development was almost equivalent to the EU’s in 2022, this changed in 2023. Inflation in the UK remained above 10% until April 2023, at which point inflation was at 10% or higher for almost an entire year. Nonetheless, UK inflation also came down later in 2023 and reached the 4% mark at the end of December 2023. Based on the overall relatively similar development of inflation around the world, it is likely that inflation will stay at elevated levels in the short term. Another key reason for relatively stale inflation is that central banks stopped hiking their interest rate for a while now in 2023. Figure 1 summarizes the development of inflation in the US, EU, and the UK.
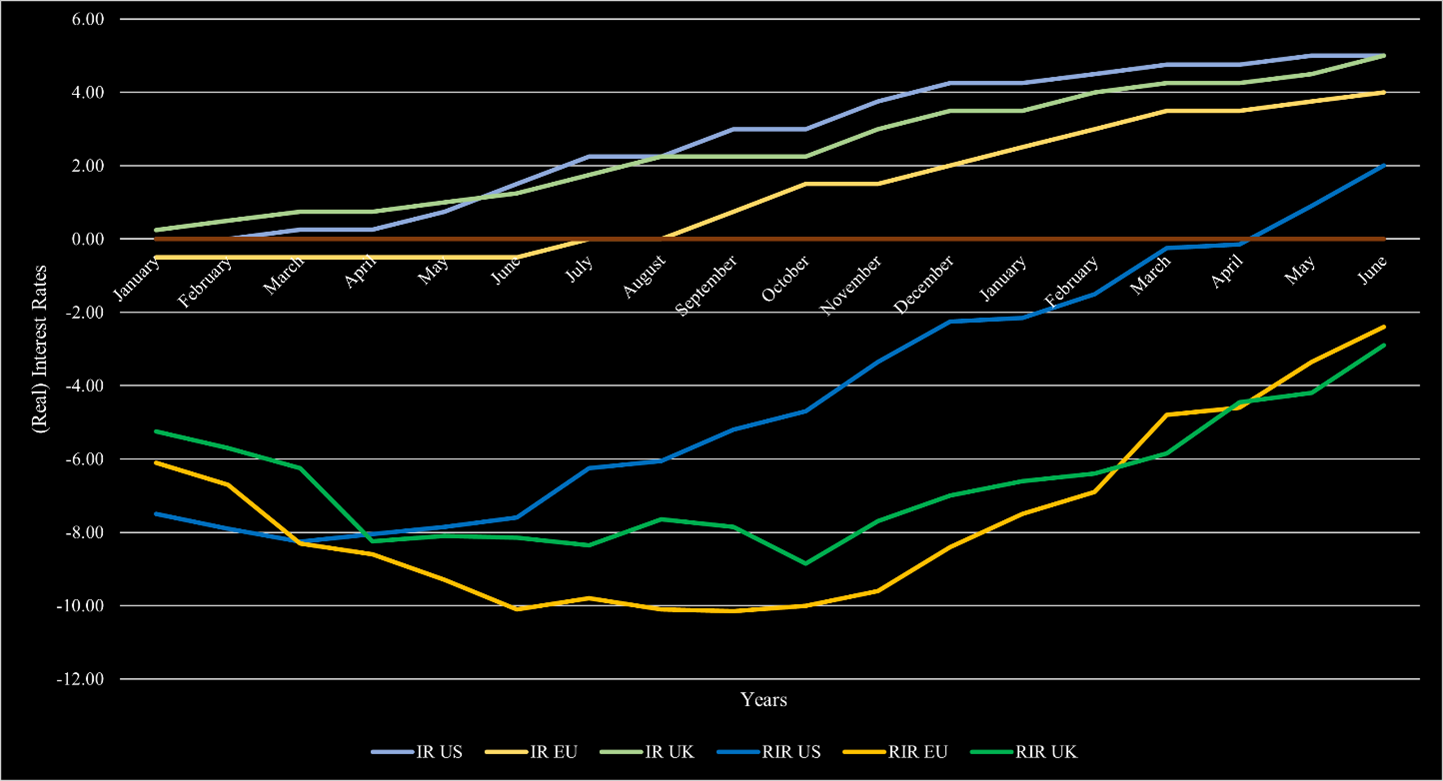
With the soaring inflation in 2021 and afterward, central banks had to react. Financial markets enjoyed rates close to zero, if not negative, for a long time. As a response, central banks started raising their interest rates. The Bank of England was the first to raise its interest rates in December 2021. The Fed followed in March 2022 and hiked its rate in every meeting and by a higher amount on average than the BoE or the ECB. The BoE did so too, but did smaller hikes on average. The ECB followed in June 2022, but they did not hike at every meeting. At the start of 2023, the interest rate in the US was already at 4.25% compared to 3.5% in the UK and 2.5% in the EU. Consequentially, the ECB hiked more in 2023 but did not reach the same heights as in the US or UK, which are currently at 5.25%, while the ECB’s interest rate remains at 4.5%. With interest rates now higher than inflation rates in each of those economies, most market participants expect interest rate cuts in 2024, especially due to an elevated possibility of a recession ahead.
Inflation and interest rates have been present topics. Inflation rates have continuously decreased throughout 2023 across most economies. While this development was promising, it was necessary as inflation rates went as high as almost 12% towards the end of 2022. In the US, inflation has decreased to 3%-4% in the past few months with no particular direction since then. For 2024, it is widely expected that inflation will decrease further, albeit to a limited degree. Most market participants expect inflation to be around 2.3% by the end of 2024. Others see inflation to drop to as low as 1.6%. Assuming no further geopolitical crises and no further escalation of existing crises, inflation is unlikely to rise further than 3.5% by the end of 2024. Figure 1 shows the development of inflation rates in the US, UK, and the EU from January 2022 to the end of 2024. The general sentiment that inflation rates should fall is intuitive given the high interest rates at this time. In the EU, the development has mostly mimicked the US, but with a delay of a couple of months, due to a more restrictive central bank policy when Covid-19 emerged. Inflation in the EU has also reached a point, where inflation is no longer declining at levels slightly below 4% after being at 10% at the beginning of the year. For 2024, inflation is also expected to further fall, but not to the same degree as in the US. Expectations for inflation in the EU range from 2.6% to 4.5% with the most likely level around 3.4%. The situation in the UK also drastically improved towards the end of the year. UK’s inflation fell to 4% after lingering around the 10% mark for almost an entire year. Inflation expectations for the UK are mostly equivalent to the EU’s expectations, but its projections are more volatile based on the country’s state over the past few years.
The current macroeconomic volatility has not changed. Interest rates and inflation remain elevated. At least in most markets, the inflation rate is continuously declining. In the US, inflation reached 3% and is on its way to the upper target of 2% in the short-term. Europe is following this development but still has a substantial way ahead before inflation will eventually reach those levels, as inflation remains at 6.4%. In the UK, the situation is more dire and inflation declined to 7.9% after being above 10% since August 2022. In order to bring inflation levels down, central banks have hiked substantially over the past 1.5 years. In the US, the federal fund rate is now above 5.25% with the most recent hike, which has largely been deemed unnecessary by market participants. The ECB also increased its interest rate by 25bps and is now at 4.25%. The BoE also raised its core interest rate by 25bps in their latest meeting and is now equivalent to the US’s 5.25%. The US also reached the status of positive real interest rates since the hikes started. Europe and the UK are following this trend but have not reached this territory yet. Figure 1 also shows how Europe and the UK are lacking behind the US. In the current environment, a recession is still likely. While projections have changed throughout the year, the consensus opinion remains that there will likely be a short and with a shallow to medium impact on the economy. The most notable change is that the recession expectation has pushed further and further into the future. It started with estimations that it will happen by mid-2023, then towards the end of 2023. Now, most estimates place the recession somewhen in 2024.
From a financial perspective, inflation, interest rates, and a possible recession remain the most vital topics in the short term. While inflation came down substantially in 2023, interest rate hikes have persisted thus far. In the US, the interest rate set by the Fed remains at 5% after they decided that no hike was necessary in June 2023. With the release of job data in early July, talks about further hikes have increased, as data showed that job growth has slowed. Market participants now expect further hikes in 2023. The projection from the beginning of 2023 and possible rate cuts as early as Q3 2023 seem very unlikely at this point. Figure 1 shows the expected interest rate level until 2025. Rates are expected to rise to 5.5% by the end of 2023. Based on a survey from 18 members of the FOMC, rate projections range from 5.1%-6.1% by the end of the year. In 2024 and onwards, gradual rate cuts are expected with rates around 3% by 2025. These projections are highly dependent on a positive development of inflation and job data. Recent inflation data in the US has been very promising, as inflation decreased to “only” 4%. The steep measures taken by the Fed since 2022 managed to combat inflation substantially. Excluding highly impactful developments (e.g., a steep recession or a strong escalation of war), inflation is expected to steadily decrease over the next years. By the end of 2023, inflation is expected to be around 3% ± 1% and slightly above 2% ± 2% in 2024. The expected, slowed decrease in inflation is largely attributed to the tamer measures of the Fed after their initial aggressive hikes. As these take time to become effective, the decrease should slow down. Additionally, a recession or a market correction is highly likely which may cause further issues with inflation and may slow down the effectiveness of the measure so far. Overall, the likelihood of a recession is still significantly high. The most notable differences in the expected recession compared to forecasts in early 2023 and 2022 are the recession is likely a mild one. Additionally, with the recent positive developments, a possible recession is pushed further in the future. At the end of 2022, a recession was anticipated to occur between Q3 and Q4 2023. Current forecasts expect a recession in the US in early 2024. Despite the harsh ecosystem, US equities had a great year in 2023 with a 15% return so far. On an industry level, the picture looks very different. Basically the entire gain of equities came from soaring tech stocks. On the other end of the spectrum are banking stocks, which have suffered this year, especially after the collapse of multiple large banks, such as Silicon Valley Bank and Credit Suisse. Forecasts for the value of the S&P 500 at the end of 2023 deviate substantially. In general, estimates were raised slightly compared to estimates back in 2022. On an aggregate level, investment banks expect the S&P 500 to end the year at roughly above 4,100. The highest estimates are 4,550 for the index. Contributors to these estimates are a less aggressive Fed, resilient economic growth, and the recent interest in artificial intelligence in combination with the soaring tech stocks. Bearish outlooks go as low as 3,400 points and cite a continued slide in stocks as the core reason.
|
|
|
Stone Mountain Capital LTD is authorised and regulated with FRN: 929802 by the Financial Conduct Authority (‘FCA’) in the United Kingdom. The website content is neither an offer to sell nor a solicitation of an offer to buy an interest in any investment or advisory service by Stone Mountain Capital LTD and should be read with the DISCLAIMER. © 2024 Stone Mountain Capital LTD. All rights reserved. |





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
